In the intricate landscape of modern electronics, where components shrink and performance demands soar, the **Surface Mount Device (SMD) Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor**, often called a **Chip Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor**, stands as a crucial workhorse. These compact cylinders, dotting our circuit boards, deliver the essential energy storage and filtering required for countless devices, from smartphones to industrial drives.
Their dominance stems from compelling advantages tailored to contemporary manufacturing and design:
1. Space Savior: Their low-profile, surface-mount design is indispensable for densely packed PCBs, freeing up valuable real estate compared to bulky through-hole counterparts.
2. Automation Ally: Perfectly suited for high-speed pick-and-place machines, SMD capacitors streamline assembly, significantly boosting production efficiency and reducing costs.
3. High-Capacity Champion (for their size): Like all aluminum electrolytics, they offer the highest capacitance values per unit volume compared to ceramic or film capacitors in the SMD realm, making them ideal for significant energy storage needs like power supply bulk filtering.
4. Cost-Effective Power: They provide a very economical solution for achieving high capacitance values in demanding voltage scenarios.
The core technology remains similar to traditional aluminum electrolytics:
* Anode: A high-purity aluminum foil, chemically etched to increase surface area, then anodized to form a thin, insulating aluminum oxide layer (`Al₂O₃`) – the critical dielectric.
* Cathode: A conductive liquid electrolyte (or increasingly, solid conductive polymer) impregnating a separator paper, in contact with a second aluminum foil (cathode foil).
* Construction: These elements are wound into a compact cylinder.
* Encapsulation: The wound element is sealed within an aluminum can (case), typically marked with capacitance, voltage, and polarity. The base provides SMD solder terminals, clearly indicating the negative (cathode) side.
Understanding these parameters is vital for optimal selection:
* Capacitance (C): Ranges widely, from microfarads (µF) to thousands of µF. SMD versions typically have a lower maximum capacitance than equivalent-sized through-hole parts.
* Rated Voltage (V): Specifies the maximum continuous DC voltage. Common ranges span from a few volts to several hundred volts.
* Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR): A critical parameter, especially in switching power supplies. Lower ESR means less energy loss as heat and better high-frequency performance. Polymer types generally offer significantly lower ESR than liquid electrolyte types.
* Ripple Current Rating: The maximum AC current (specified at a frequency, often 100/120Hz) the capacitor can handle without exceeding its temperature limits. Exceeding this rating drastically shortens lifespan.
* Lifetime: Rated at a specific temperature (e.g., 2000 hours @ 105°C). Temperature is the primary aging factor – operating well below the rated temperature dramatically extends usable life.
* Polarity: Absolute Attention Required! Reverse voltage connection causes rapid failure, often catastrophic. The negative terminal is distinctly marked on the package.
* Temperature Range: Standard ratings cover -40°C / -55°C to +85°C / +105°C / +125°C. Performance degrades at temperature extremes.
SMD Aluminum Electrolytics are fundamental in:
1. Power Supply Filtering: Bulk energy storage and smoothing ripple in DC/DC converters, AC/DC adapters, and VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) – especially on the output stage.
2. Decoupling: Stabilizing power rails near ICs (though often supplemented by ceramics for very high frequencies).
3. Energy Reservoir: Providing short-term power bursts or holding up voltage during brief interruptions.
4. Audio Circuits: Coupling and filtering in audio amplifiers and devices (though ESR and non-ideal characteristics need consideration).
5. Consumer Electronics, Computing, Automotive Electronics, Industrial Controls: Found virtually everywhere robust energy storage is needed in a compact form factor.
1. Required Capacitance & Voltage: The fundamental starting point.
2. ESR Needs: Critical for high-ripple-current applications like switch-mode power supplies. Lower ESR is generally better for performance and thermal management.
3. Ripple Current Rating: Must meet or exceed the circuit's worst-case ripple current.
4. Operating Temperature: Choose a rating exceeding your application's maximum ambient temperature plus internal heating. Derating voltage at high temperatures is often recommended.
5. Size Constraints: Select the appropriate case size (e.g., EIA metric codes like 6.3x5.4mm, 8x6.5mm, 10x10mm)
6. Lifetime Requirement: Ensure the rated lifetime at your operating temperature meets the product's lifespan goals.
7. Electrolyte Type: Liquid electrolyte (standard) vs. Conductive Polymer. Polymer offers much lower ESR, longer life, higher stability, but often at a higher cost and potentially lower maximum voltage ratings.
* Limited Capacitance/Voltage Range (vs Through-Hole): SMD packages constrain maximum achievable values.
* Finite Lifetime: Degrades predictably over time, accelerated by heat.
* ESR: Generally higher than ceramic capacitors, especially at high frequencies. Liquid types have significantly higher ESR than polymer.
* Polarity Sensitivity: Incorrect installation causes immediate failure.
* Voltage Derating: Often necessary for reliability, especially at high temperatures.
The SMD Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor is a cornerstone of modern electronic design, masterfully balancing significant capacitance, voltage handling, and compact size for surface-mount assembly. While mindful of their limitations like polarity sensitivity and finite lifetime, understanding their characteristics and selecting the right type (standard liquid or advanced polymer) empowers designers to create efficient, reliable, and compact power solutions that drive the devices we rely on daily. Their enduring presence on our circuit boards is a testament to their indispensable role in the electronic ecosystem.
Topdiode produces high-quality SMD Aluminum for cross over,
Following cross reference chart FYI.
|
Description |
UF Capacitors |
Rubycon |
Samwha |
Nippon |
Yageo |
Nichicon |
Panasonic |
|
TCS 85C V-Chip Aluminum Electrolytic |
TCS Series |
SEV Series |
SC Series |
MVA Series |
CA Series |
UWX Series |
EEE-X(A)S Series |
|
TCK 105C V-Chip Aluminum Electrolytic |
TCK Series |
SKV Series |
RC Series |
MVE Series |
CB Series |
UWT Series |
EEEHA Series |
|
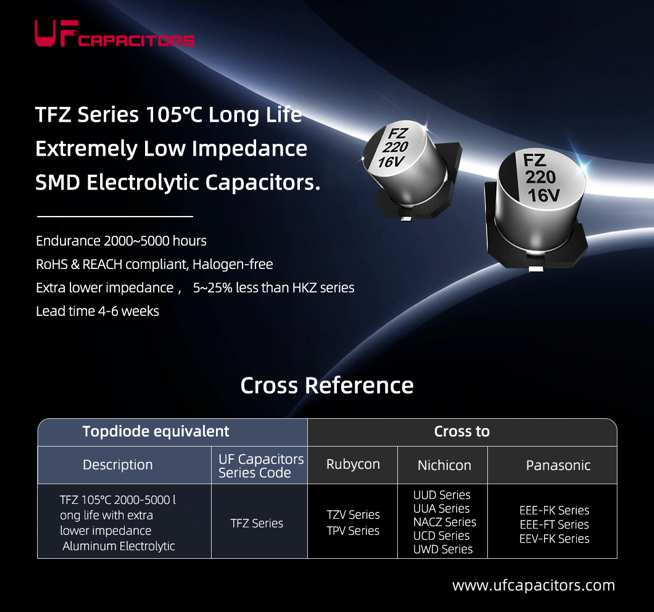
TFZ 105C 2000-5000 long life with extra lower impedance Aluminum Electrolytic |
TFZ Series |
TZV Series |
CM Series |
MZA Series |
*** |
UUD Series |
EEE-FK Series |
|
TLZ 105C 1000-2000h |
TLZ Series |
SZV Series |
*** |
MVY Series |
*** |
UCL Series |
EEE-FC Series |
|
TMA 105C 2000h conductive polymer aluminum solid Aluminum Electrolytic |
TMA Series |
PAV Series |
FA Series |
PXE Series |
*** |
CV Series |
SVPE Series |
|
TMB Series 105C 2000h conductive polymer aluminum solid Aluminum Electrolytic |
TMB Series |
PAV Series |
FA Series |
PXE Series |
*** |
CV Series |
SVPC Series |
If you want to explore more component,
please visit our website:https://www.topdiodes.com
Or send inquiry to : Carey@topdiode.com